Fungal infections can affect anyone and range from minor skin irritations to more severe internal infections.
The two primary treatment options are topical and oral antifungal medications, each with its advantages and limitations.
In this article, we’ll explore the differences, benefits, and drawbacks of topical and oral antifungal treatments, helping you choose the best option for your specific needs.
What are Fungal Infections?
Fungal infections are caused by the overgrowth of fungi on or inside the body, leading to conditions like athlete’s foot, ringworm, nail fungus, and yeast infections.
Depending on the infection type and its location, the right treatment can vary significantly.
Book Your Skin Consultation with Dr. Harmandeep Sidhu
Trusted dermatologist in Chandigarh. Get expert care in skin, hair and lasers at Athena Skin Clinic.

Common Types of Fungal Infections:
- Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis): Affects the feet, causing itching, redness, and peeling.
- Ringworm (Tinea Corporis): Appears as ring-shaped rashes on the skin, highly contagious.
- Nail Fungus (Onychomycosis): Leads to thick, discolored, and brittle nails.
- Yeast Infections (Candidiasis): Often occurs in moist areas like underarms or between skin folds.
- Scalp Fungus (Tinea Capitis): Affects the scalp, causing hair loss and scaly patches.
The choice between topical and oral antifungal treatment depends on the type, location, and severity of the infection.
What Are Topical Antifungal Medications?
Topical Antifungals are applied directly to the skin or affected area and come in various forms, including creams, lotions, ointments, and sprays. They are commonly used for localized, mild infections and are available both over-the-counter (OTC) and by prescription.
How They Work:
Topical antifungal medications work by disrupting the fungal cell membrane, preventing fungal growth and eventually eradicating the infection on the skin’s surface.
Common Active Ingredients:
- Clotrimazole: Often used for athlete’s foot, jock itch, and ringworm.
- Miconazole: Effective for various skin infections, including yeast infections.
- Terbinafine: Commonly used for athlete’s foot and nail fungus.
- Ketoconazole: A prescription-strength option for resistant infections.
Infections Treated with Topical Antifungals:
- Mild cases of athlete’s foot
- Ringworm on the skin
- Yeast infections on the skin
- Jock itch
- Fungal skin infections on hands and body
Advantages of Topical Antifungals:
- Targeted Application: Applied directly to the infection site, reducing systemic effects.
- Minimal Side Effects: Generally well-tolerated with fewer side effects compared to oral medications.
- Over-the-Counter Options: Many are available without a prescription, making them easy to access.
- Safe for All Ages: Can be used on children and adults with minor fungal infections.
Drawbacks of Topical Antifungals:
- Limited Effectiveness for Severe Infections: Not suitable for deep or extensive infections.
- Frequent Application Needed: Often requires application multiple times a day for several weeks.
- Less Effective on Thick Skin or Nails: Struggles to penetrate nail beds or thickened skin affected by fungal infections.
What Are Oral Antifungal Medications?
Oral Antifungals are taken in pill or liquid form and circulate throughout the body via the bloodstream. They are commonly prescribed for severe, widespread, or deeply embedded fungal infections that topical treatments cannot adequately address.
How They Work:
Oral antifungal medications work systemically, targeting fungi from within the body. They are effective for infections that affect nails, the scalp, or internal organs, areas where topical medications are less effective.
Common Oral Antifungal Medications:
- Fluconazole: Often used for yeast infections and some skin infections.
- Itraconazole: Used for nail fungus and systemic fungal infections.
- Terbinafine: Effective for nail fungus, athlete’s foot, and scalp infections.
- Griseofulvin: Commonly used for scalp and nail infections.
Infections Treated with Oral Antifungals:
- Nail fungus (Onychomycosis)
- Scalp infections (Tinea Capitis)
- Systemic fungal infections
- Severe or widespread skin infections
- Chronic or recurrent yeast infections
Advantages of Oral Antifungals:
- Systemic Treatment: Reaches infections throughout the body, ideal for hard-to-reach or deep infections.
- Fast and Effective for Tough Cases: Often provides quicker relief for stubborn or widespread infections.
- Convenience: Typically requires only a once-daily dose, making it easier to comply with long-term treatment.
Drawbacks of Oral Antifungals:
- Potential Side Effects: May cause digestive upset, headaches, or, in rare cases, liver toxicity.
- Medical Supervision Required: Long-term use requires liver function monitoring, especially with medications like itraconazole and terbinafine.
- Higher Cost: Oral antifungals are often more expensive than topical treatments and may not be fully covered by insurance.
Topical vs. Oral Antifungal Treatments: Key Differences
| Aspect | Topical Antifungals | Oral Antifungals |
| Application | Directly on the infected area | Taken orally (pills, capsules, or liquids) |
| Effectiveness | Best for mild or localized infections | Best for severe, widespread, or internal infections |
| Side Effects | Minimal; mostly skin irritation | Higher risk of systemic side effects |
| Treatment Duration | Several weeks, sometimes months | Generally shorter for mild infections |
| Medical Supervision | Rarely needed | Often required for monitoring |
| Cost and Accessibility | Usually affordable and available OTC | Prescription-based, generally more expensive |
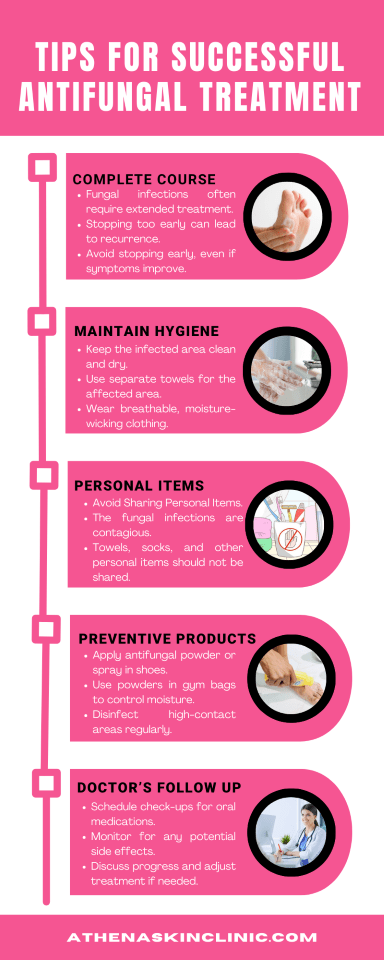
Tips for Successful Antifungal Treatment
- Complete the Full Course: Fungal infections often require extended treatment. Stopping too early can lead to recurrence.
- Maintain Hygiene: Keep the infected area clean and dry to prevent fungal growth.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Fungal infections are contagious. Towels, socks, and other personal items should not be shared.
- Use Preventive Products: For those prone to infections, consider using antifungal powders or sprays in high-risk areas, such as shoes or gym bags.
- Follow Up with Your Doctor: For prescription oral medications, regular check-ups may be necessary to monitor for side effects.
Conclusion: Finding the Right Solution for You
Choosing between topical and oral antifungal medications depends on the specific infection, its severity, and your overall health. For mild, localized infections, topical treatments are generally effective and safe.
However, for severe, chronic, or internal infections, oral antifungals offer a more potent solution.
Consulting with a dermatologist near you can help ensure the best treatment for your situation, leading to quicker, more effective relief.